Definition and difference of Layer 2 and Layer 3 managed network switches
We are used to saying that in a layer 2 network environment, the same vlan can communicate with each other, but different vlans cannot communicate. If you want to communicate, you must use a layer 3 device, so the thing that a layer 3 switch must do is routing and forwarding.
What is the specific difference between the three-layer switch?
Layer 2 switches work on Layer 2 (data link layer) of the OSI model, so they are called Layer 2 switches.
The development of Layer 2 switching technology is relatively mature. Layer 2 switches are data link layer devices that can identify the MAC address information in the data packet, forward it according to the MAC address, and record these MAC addresses and corresponding ports in an internal address. table. The specific workflow is as follows:
(1) When the switch receives a data packet from a certain port, it first reads the source MAC address in the packet header, so that it knows which port the machine with the source MAC address is connected to;
(2) Then read the destination MAC address in the packet header, and look up the corresponding port in the address table;
(3) If there is a port corresponding to the destination MAC address in the table, copy the data packet directly to this port;
(4) If the corresponding port cannot be found in the table, the data packet will be broadcast to all ports. When the destination machine responds to the source machine, the switch can learn which port the destination MAC address corresponds to. It is no longer necessary to broadcast to all ports.
This process is continuously cycled, and the MAC address information of the entire network can be learned. This is how a Layer 2 switch establishes and maintains its own address table.
Layer 2 switching technology has developed from bridge to VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network), and has been widely used in LAN construction and transformation. The second layer switching technology is the second layer in the OSI seven-layer network model, that is, the data link layer. It forwards according to the destination MAC address of the received data packet, which is transparent to the network layer or high-level protocols. It does not deal with the IP address of the network layer, and does not deal with the port addresses of high-level protocols such as TCP and UDP. It only needs the physical address of the data packet, that is, the MAC address. The data exchange is realized by hardware, and its speed is quite fast. This is A significant advantage of Layer 2 switching. However, it cannot handle data exchange between different IP subnets. Traditional routers can handle a large number of data packets across IP subnets, but their forwarding efficiency is lower than that of the second layer. Technology was born.
Layer-3 switching is known as multi-layer switching technology, or IP switching technology.
As we all know, the traditional switching technology operates on the 2 layer of the OSI network standard model - the data link layer, while the t3-layer switching technology realizes the high-speed forwarding of data packets on the third layer of the network model. Simply put, the 3-layer switching technology is: 2-layer switching technology + 3-layer forwarding technology.
A Layer 3 switch is a switch with some router functions.
The most important purpose of the three-layer switch is to speed up the data exchange within the large local area network. The routing function it has is also for this purpose, and it can achieve one routing and multiple forwarding. Regular processes such as data packet forwarding are implemented by hardware at high speed, while functions such as routing information update, routing table maintenance, routing calculation, and routing determination are implemented by software. Layer 3 switching technology is Layer 2 switching technology + Layer 3 forwarding technology.
The emergence of three-layer switching technology solves the situation that after the network segment is divided in the LAN, the subnet in the network segment must rely on the router for management, and solves the network bottleneck problem caused by the low speed and complexity of the traditional router.
Does the switch have to check the routing table when it determines that the destination IP is not its own? No, this is the key to the switch. The switch will not check the routing table, the arp table, or the mac address table at this time; what table will the switch check?
At this time, the switch will check the hardware forwarding table integrated in the ASIC hardware forwarding card. What does this hardware forwarding table contain?
When the first packet comes, it is found that the hardware forwarding table does not have any entries, so the data packet must be handed over to the routing process at this time. Once it is handed over to the CPU for processing, CPU resources will inevitably be consumed. At this time, the routing table will be checked. , and then found that this IP address is directly connected to itself, then check arp to find the mac address corresponding to this address, and then forward it out
In the process of deciding to forward, the switch will do at least three things. First, modify the ttl value of the IP header; second, modify the original mac address and change it to the mac address of its own outgoing interface; third, establish a switch hardware forwarding table, including the destination IP address, the mac address corresponding to the destination IP address (next hop), the vlan corresponding to the mac address, and the corresponding port (each manufacturer has its own understanding)
In this way, when a packet arrives, the switch will check the hardware forwarding table and forward it directly without going through the routing table query, that is, the principle of one route of the switch and multiple switches.
In short, Layer 2 switches are used in small local area networks. Needless to say, in a small local area network, broadcast packets have little effect. The fast switching function, multiple access ports and low price of the layer 2 switch provide a perfect solution for small network users.
The most important function of the three-layer switch is to speed up the fast forwarding of data within the large local area network, and the addition of the routing function also serves this purpose. If a large network is divided into small local area networks according to factors such as departments and regions, this will lead to a large number of Internet accesses, and the simple use of Layer 2 switches cannot achieve Internet access; such as the simple use of routers, due to the limited number of interfaces and The slow routing and forwarding speed will limit the speed and network scale of the network, so it is the first choice to use a layer-3 switch with routing function and fast forwarding.
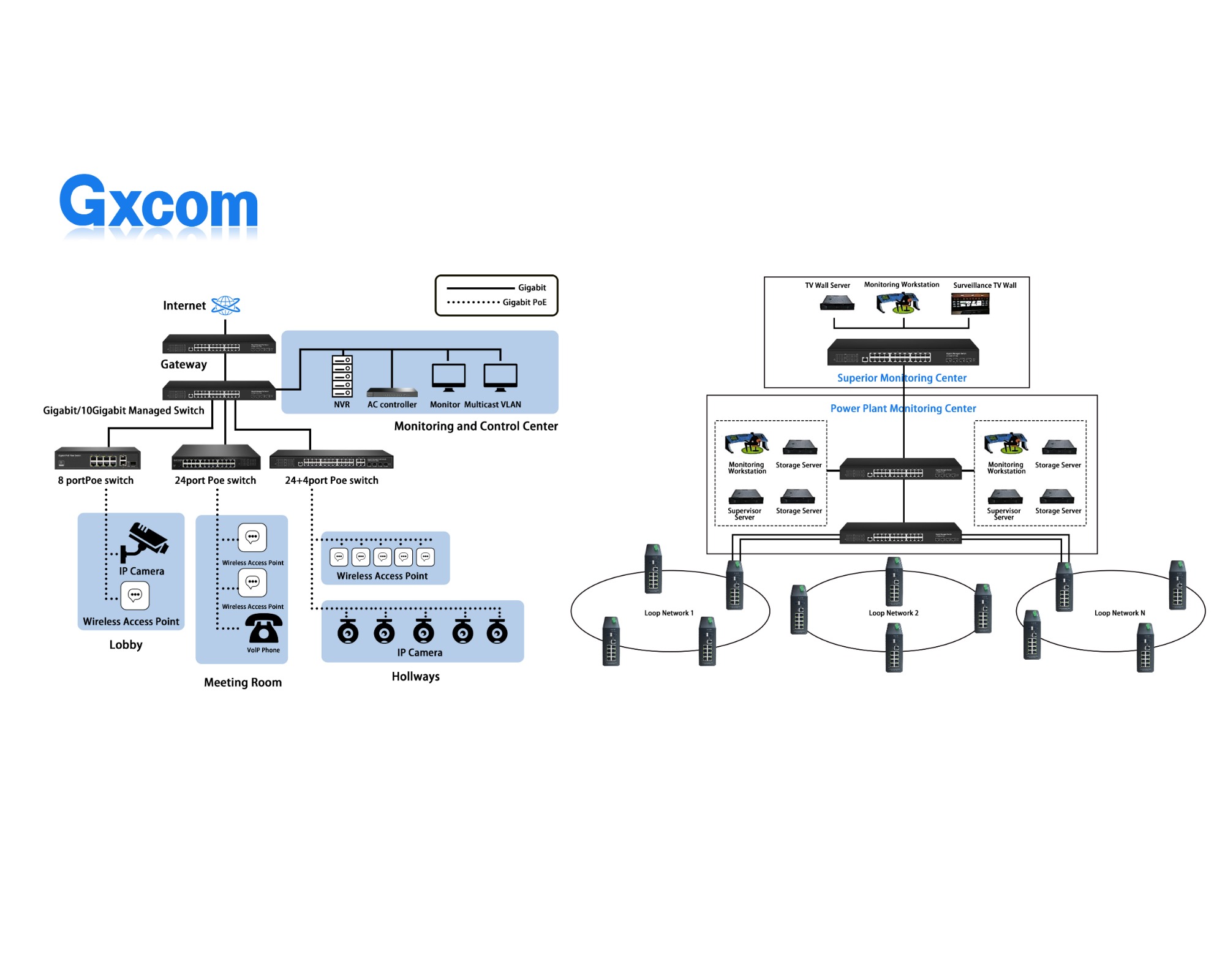
Generally speaking, in the network where the internal network data traffic is large and fast forwarding response is required, if all the work is done by layer 3 switches, the burden of layer 3 switches will be overloaded, the response speed will be affected, and the routing between the networks will be switched. It is a good networking strategy to use routers to make full use of the advantages of different devices. Of course, the premise is that your budget is sufficient. Otherwise, the next best thing is to let the three-layer switch also serve as Internet interconnection.
The traditional switching technology operates on the 2 layer of the OSI network standard model - the data link layer, while the 3 layer switching technology realizes the high-speed forwarding of data packets on the third layer of the network model, which can realize the network routing function , and can achieve optimal network performance according to different network conditions.


 Do I need a managed switch for PoE cameras?
Do I need a managed switch for PoE cameras?
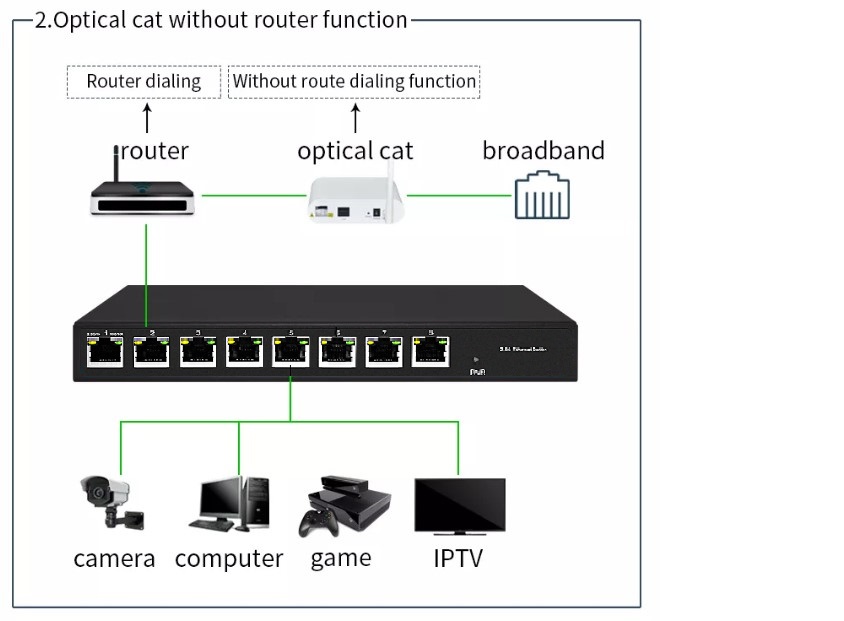 How to do PoE troubleshooting?
How to do PoE troubleshooting?
 SFP Compatibility Guide and How to Use a Compatible SFP Module?
SFP Compatibility Guide and How to Use a Compatible SFP Module?