The application and significance of L3 switches in campus networks and metropolitan education networks
With the development of network technology, the term "Layer 3 switch" has become more popular in the industry. In large and medium-sized networks, there are already many Gigabit Layer 3 switches and even 10 Gigabit Layer 3 switches in the core network. . So, how much do you know about Layer 3 switches?
In short, Layer 3 switching uses Layer 3 switching technology to realize communication between VLANs, that is: Layer 3 switching = Layer 2 switching + Layer 3 forwarding.
Working principle of three-layer switching
1. When a layer 3 device receives a data frame, it will disassemble the original data frame and re-encapsulate the new source MAC address and destination MAC address. And because the information in the frame header changes, the final frame check CRC should also follow. Change.
2. Among the multiple data packets in this flow, only the first data packet is processed by the Layer 3 engine of the Layer 3 switch. The processing method is software. The same as the router, the Layer 3 engine obtains new Layer 2 encapsulates the information and routes the packet.
3. After the forwarding of the first data packet is completed, an MLS entry is created in the hardware for subsequent re-encapsulation and fast forwarding of data packets performed by the hardware. Layer 2 data frames will be re-encapsulated into the frame format of the next network segment that needs to be forwarded. This is the principle of MLS "once routing, many switching".
4. The key to MLS based on CEF (a topology-based forwarding model) is two forwarding information tables. The forwarding information base (FIB) corresponds to the routing table one-to-one and is a mirror image of the routing table. When the routing table is updated, the FIB changes accordingly. The FIB contains the corresponding relationship between the IP address of the adjacent host and the VLANID. The adjacency table contains the correspondence between adjacent hosts and switch MAC addresses to provide Layer 2 rewriting information.
5. The MLS forwarding process based on CEF, that is, sending unicast data packets, re-encapsulating the data frame by searching the FIB and adjacency table, and forwarding it from the corresponding port.
Advantages of using layer 3 switches
In addition to excellent performance, Layer 3 switches also have some features that traditional Layer 2 switches do not have. These features can bring many benefits to the construction of campus networks and metropolitan education networks.
1. High scalability
When a Layer 3 switch connects multiple subnets, the subnets only establish logical connections with the Layer 3 switching modules. They do not need to add ports like traditional external routers, thus protecting users' investments in campus networks and metropolitan education networks. And meet the rapid growth needs of school network applications in 3-5 years.
2. High cost performance
Layer 3 switches have the ability to connect large networks, and their functions can basically replace some traditional routers, but the price is close to that of layer 2 switches. Nowadays, the price of a Gigabit Layer 3 switch is only a few thousand yuan, which is about the same as the price of a high-end Layer 2 switch.
3. Built-in security mechanism
Layer 3 switches can have the same access list function as ordinary routers, and can realize one-way or two-way communication between different VLANs. If set up in the access list, users can be restricted from accessing specific IP addresses, so schools can ban students from accessing unhealthy sites.
Access lists can not only be used to prohibit internal users from accessing certain sites, but can also be used to prevent illegal users outside the campus network and metropolitan education network from accessing network resources within the campus network and metropolitan education network, thereby improving network security.
4. Suitable for multimedia transmission
Educational networks often need to transmit multimedia information, which is a feature of education networks. Layer 3 switches have QoS (Quality of Service) control functions and can allocate different bandwidths to different applications.
For example, when transmitting video streams on campus networks or metropolitan education networks, a certain amount of dedicated bandwidth can be reserved specifically for video transmission, which is equivalent to opening up a dedicated channel in the network. Other applications cannot occupy these reserved bandwidths. bandwidth, thus ensuring the stability of video streaming transmission. Ordinary layer 2 switches do not have this feature, so when transmitting video data, the video will jitter at times of speed and speed.
In addition, video on demand (VOD) is also a frequently used service in education networks. However, because some video on demand systems use broadcasts for transmission, and broadcast packets cannot be implemented across network segments, VOD cannot be implemented across network segments; if VOD is implemented in unicast form, although it can be implemented across network segments, it does not support The number of simultaneous connections is very small, and generally dozens of connections occupy all the bandwidth. The three-layer switch has a multicast function, and VOD data packets are sent to various subnets in the form of multicast, which not only realizes cross-network segment transmission, but also ensures the performance of VOD.
5. Billing function
In university campus networks and metropolitan education networks in some areas, there may be a need for billing, because the three-layer switch can identify the IP address information in the data packets, so it can count the data traffic of the computers in the network and calculate the flow rate. You can also count the time the computer is connected to the network and bill based on time. It is difficult for ordinary layer 2 switches to do both of these things at the same time.
 Do I need a managed switch for PoE cameras?
Do I need a managed switch for PoE cameras?
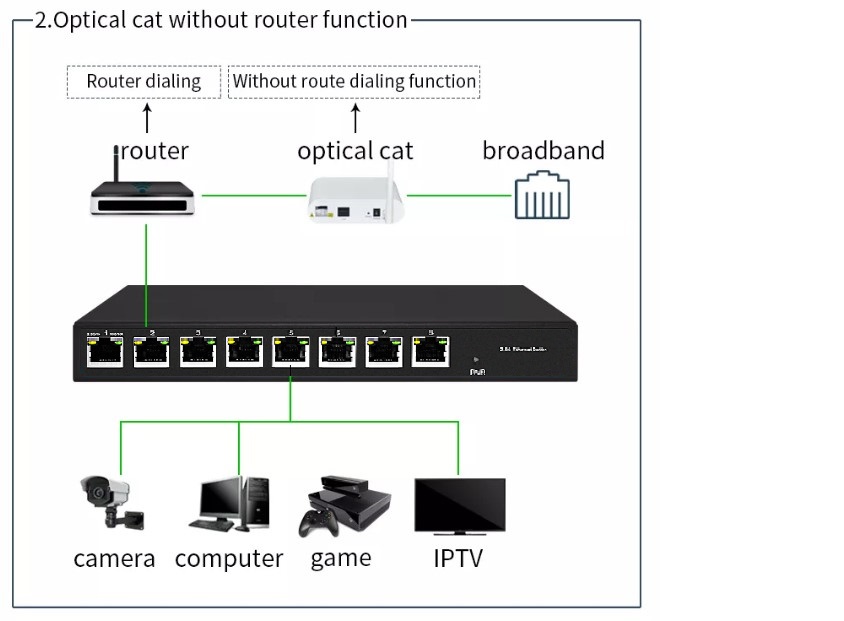 How to do PoE troubleshooting?
How to do PoE troubleshooting?
 SFP Compatibility Guide and How to Use a Compatible SFP Module?
SFP Compatibility Guide and How to Use a Compatible SFP Module?